“This study introduces PheSeq, a Bayesian deep learning model designed to integrate p-value data from sequence analysis with phenotype descriptions from literature and network data. It improves the robustness and interpretability of gene-disease association studies.”
这项研究介绍了PheSeq,这是一种贝叶斯深度学习模型,旨在将序列分析中的P值数据与文献中的表型描述和网络数据结合起来。它提高了基因与疾病关联研究的稳健性和可解释性。
Behind the paper [1]: (https://genomemedicine.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13073-024-01330-7)
Highlights:
- The Bayesian deep learning framework successfully bridges the phenotype description perception and association significance (p-value) in the gene-disease association studies.
- Deep learning is used to derive embeddings for phenotype descriptions from literature and network data.
- The framework treats the p-value as a weak supervised signal in the uncertainty inference.
- A probability graphical model effectively bridges the aforementioned heterogeneous data modalities by activating a switch when there is consistency between the association significance and the phenotype description.
译文(KIMI大模型网页免费版):
- 贝叶斯深度学习框架成功地在基因与疾病关联研究中架起了表型描述感知与关联显著性(P值)之间的桥梁。
- 深度学习被用来从文献和网络数据中派生表型描述的嵌入。
- 该框架将P值视为不确定性推断中的弱监督信号。
- 一个概率图模型通过在关联显著性与表型描述之间存在一致性时激活一个开关,有效地桥接了上述异构数据模态。
In the scenario of genotype-phenotype association studies, p-values from various sequence analyses such as GWAS and RNA-seq provide a measure of significance. However, these p-values often come with high uncertainty and lack of interpretability.
译文(KIMI大模型网页免费版):在基因型-表型关联研究的场景中,来自GWAS(全基因组关联研究)和RNA-seq(RNA测序)等各种序列分析的P值提供了一种显著性度量。然而,这些P值通常伴随着高度不确定性和解释性不足。
The proposed PheSeq model addresses these challenges by combining p-value data with deep learning-derived phenotype embeddings from literature and network data, and bridging two types of heterogeneous association data, thus enhancing the robustness and interpretability of the results.
译文(KIMI大模型网页免费版):提出的PheSeq模型通过将P值数据与来自文献和网络数据的深度学习派生的表型嵌入相结合,并桥接两种类型的异构关联数据,从而增强了结果的稳健性和可解释性。
The figure outlines the framework of the Bayesian deep learning model, PheSeq.
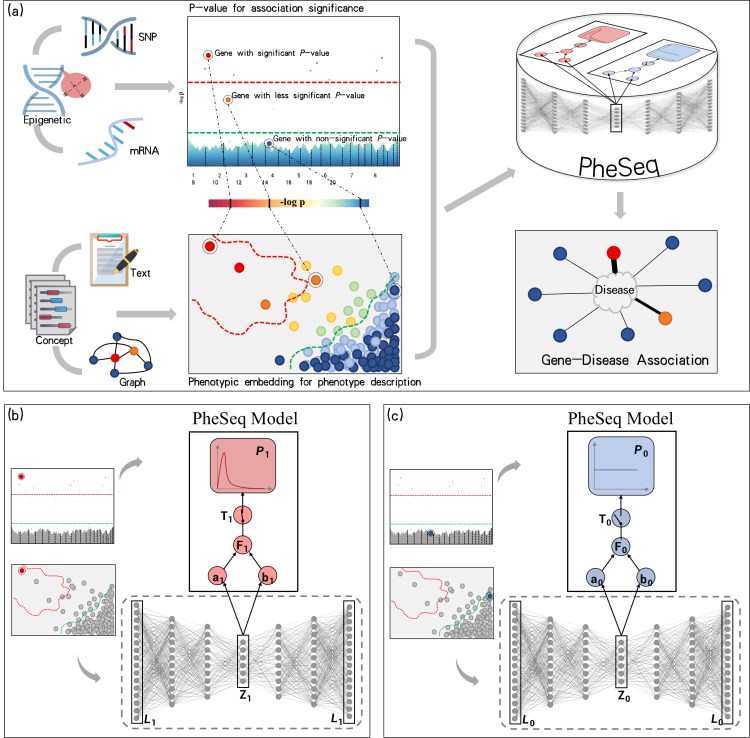
a. General model input in PheSeq involves p-values for association significance in sequence analysis and phenotypic embeddings for phenotype description from texts or graphs. The associations with p-values are graphically depicted in a Manhattan-style plot. A threshold line with a strict criterion (red line) or a less strict criterion (green line) is then applied. Concurrently, a DL perception module learns the association description of gene-disease association from text or graph. Genes exhibiting significant association descriptions tend to aggregate in the top-left region of the semantic space, as shown in the figure. Analogous patterns emerge in other scenarios. Finally, PheSeq learns the data distributions and performs data fusion for gene-disease associations.
译文(KIMI大模型网页免费版):a. PheSeq模型的一般输入包括序列分析中的关联显著性P值和来自文本或图形的表型描述的表型嵌入。带有P值的关联在曼哈顿风格的图表中图形化展示。然后应用一个严格标准(红线)或较不严格标准(绿线)的阈值线。同时,一个深度学习感知模块学习来自文本或图形的基因-疾病关联的描述。具有显著关联描述的基因倾向于在语义空间的左上区域聚集,如图中所示。在其他场景中也出现了类似的模式。最后,PheSeq学习数据分布并执行基因-疾病关联的数据融合。
b/c. Data fusion of association significance and phenotype description for a significant/non-significant gene-disease association by PheSeq. For each gene-disease association, two distinct types of observations, denoted as L for phenotypic embedding and P for p-value, are considered for data fusion. Both sets of observations are input into the PGM inference module, facilitating the learning of dependency relationships among them in conjunction with latent variables. The phenotypic embedding L is initially processed through the DL perception module for semantic training, generating high-quality embeddings denoted as Z. The latent variable T serves a pivotal role in synchronizing the phenotypic embedding data with the p-value data, the latter adhering to a beta distribution indicative of a predisposition toward“small-p-value.” In addition, another latent variable F functions as an association score, establishing connections among model parameters. Conceptually, the switch mechanism activates when both the association significance and phenotype description align, effectively bridging the above heterogeneous data modalities. Part c shows the converse situation, wherein the data indicate non-significance for the gene-disease association. In this case, a uniform distribution is employed to characterize the distribution of the p-value. The remaining configurations of the model remain consistent.
译文(KIMI大模型网页免费版):b/c. PheSeq通过数据融合对显著/不显著的基因-疾病关联的关联显著性和表型描述进行处理。对于每个基因-疾病关联,考虑了两种不同的观察类型,分别用L表示表型嵌入和P表示P值,以进行数据融合。这两组观察结果都输入到PGM(概率图模型)推理模块中,有助于学习它们与潜在变量之间的依赖关系。表型嵌入L首先通过深度学习感知模块进行语义训练,生成高质量的嵌入,表示为Z。潜在变量T在同步表型嵌入数据和P值数据中发挥关键作用,后者遵循一个beta分布,表明倾向于”小P值”。此外,另一个潜在变量F作为关联得分,建立模型参数之间的联系。从概念上讲,当关联显著性和表型描述一致时,开关机制被激活,有效地桥接了上述异构数据模态。部分c显示了相反的情况,即数据显示基因-疾病关联的非显著性。在这种情况下,采用均匀分布来描述P值的分布。模型的其余配置保持一致。
The PheSeq model was tested in three case studies involving Alzheimer’s disease (AD), breast cancer (BC), and lung cancer (LC), using GWAS, transcriptomic, and methylation data respectively. Phenotypic descriptions of the three diseases were collected from disease-related literature downloaded on a PubMed and PMC scale. Sentences that address phenotype description of the gene-disease association are filtered by a biomedical event extraction model on AGAC (Annotation of Genes with Alteration-Centric function changes [2]) corpus.
译文(KIMI大模型网页免费版):PheSeq模型在三个案例研究中进行了测试,涉及阿尔茨海默病(AD)、乳腺癌(BC)和肺癌(LC),分别使用GWAS(全基因组关联研究)、转录组学和甲基化数据。三种疾病的表型描述从PubMed和PMC规模的疾病相关文献中收集。通过AGAC(基因功能变化注释[2])语料库上的生物医学事件提取模型筛选出涉及基因-疾病关联表型描述的句子。
Finally, PheSeq identified 1024 priority genes for AD and 818 and 566 genes for BC and LC, respectively. Benefiting from data fusion, these findings represent moderate positive rates, high recall rates, and interpretation in gene-disease association studies.
译文(KIMI大模型网页免费版):最终,PheSeq为阿尔茨海默病(AD)识别了1024个优先级基因,以及分别为乳腺癌(BC)和肺癌(LC)识别了818个和566个基因。得益于数据融合,这些发现代表了中等的阳性率、高召回率以及在基因-疾病关联研究中的可解释性。
PheSeq holds particular importance in situations where a single sequence analysis may elicit systematic bias and flawed predictions of crucial genes. In such instances, PheSeq serves as an effective tool for establishing a connection between phenotype descriptions and association significance in sequence analysis and helps to recall the significant genes.
译文(KIMI大模型网页免费版):PheSeq在某些情况下具有特别的重要性,即单一序列分析可能引起系统性偏差和对关键基因的错误预测。在这些情况下,PheSeq作为一个有效的工具,帮助在序列分析中建立表型描述与关联显著性之间的联系,并有助于重新识别重要的基因。
In conclusion, this research performs a worth-trying attempt at heterogeneous association data fusion. This framework successfully bridges the phenotype description perception and p-value uncertainty inference. The association significance is utilized as a fine-grained weak signal for the association significance. Overall, it is an inspiring idea to unveil genotype-phenotype associations and investigate the potential relation dependency through data perception, data fusion, and probabilistic inference in a novel Bayesian framework.
译文(KIMI大模型网页免费版):总之,这项研究对异构关联数据融合进行了一次值得尝试的尝试。这个框架成功地桥接了表型描述感知和P值不确定性推断。关联显著性被用作关联显著性的细粒度弱信号。总的来说,这是一个鼓舞人心的想法,通过数据感知、数据融合以及在新颖的贝叶斯框架中进行概率推断,来揭示基因型-表型关联并研究潜在的关系依赖性。
Finally, we are delighted to share our work with the scientific community and domain experts in the prestigious journal, Genome Medicine. We sincerely hope that this resource can provide valuable research groundwork and further insights for the community.
译文(KIMI大模型网页免费版):最后,我们非常高兴能与科学界和领域专家分享我们的工作,发表在享有盛誉的期刊《Genome Medicine》上。我们衷心希望这个资源能为社区提供宝贵的研究基础和更深入的见解。
References
- Yao, X., Ouyang, S., Lian, Y., Peng, Q., Zhou, X., Huang, F., … & Xia, J. (2024). PheSeq, a Bayesian deep learning model to enhance and interpret the gene-disease association studies. Genome Medicine, 16(1), 56.
- Wang, Y., Zhou, K., Gachloo, M., & Xia, J. (2019, November). An overview of the active gene annotation corpus and the BioNLP OST 2019 AGAC track tasks. In Proceedings of The 5th workshop on BioNLP open shared tasks (pp. 62-71).
机器翻译-译文(KIMI大模型网页免费版)
(The blog is written by Yanhong He, Fumin Chen, Yawen Liu, Xinzhi Yao, and Jingbo Xia.)